Numerical modelling is a tool that is commonly employed in practice to aid in the design and analysis of engineering problems. Getting started with any new modelling software can be a daunting task. As experienced Irazu users, a hybrid finite-discrete element method (FDEM) modelling software, we would like to share some tips, tricks and best practices we have come across in our everyday modelling work.
Evaluate mesh quality
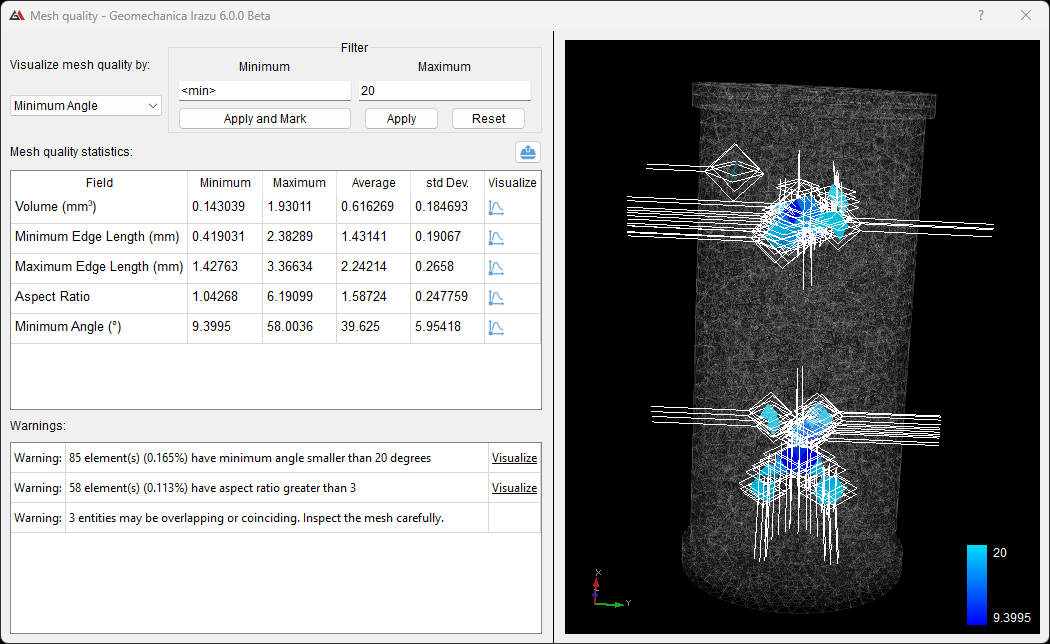
When starting a project, it is best practice to assess the mesh quality under Mesh > Mesh Quality. The tool will provide warnings for poor quality elements as well as mesh statistics. Poorly shaped elements result in lower critical time step size and can lead to numerical instability and hence erroneous results. Some suggestions to improve mesh quality are:
- Use a filter in the Mesh Quality tool to mark poor quality elements. Assess the geometry in those areas for possible issues, such as small entities, shallow intersections, or entities too close to each other.
- Reduce the element size.
- Change the meshing algorithm in Mesh > Mesh Options.
Start simple
A good tip when starting a complex modelling project, such as a hydro-thermo-mechanical coupled problem, is to start with a simple mechanical model and then gradually increase model complexity by adding one solver at a time. If possible, reduce the size of the problem to get an idea if the model is behaving correctly at the early stages of your modelling endeavor.
Import/export model properties
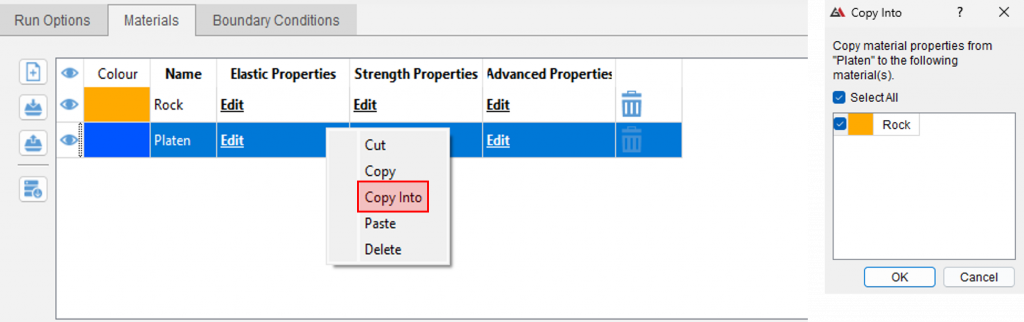
When modelling the same material or using the same boundary conditions across project files, utilize the import/export feature to save time and avoid errors when manually re-entering input parameters. In addition, using the “Copy Into” function by right-clicking a material or DFN allows the duplication of material/DFN properties into a different material set.
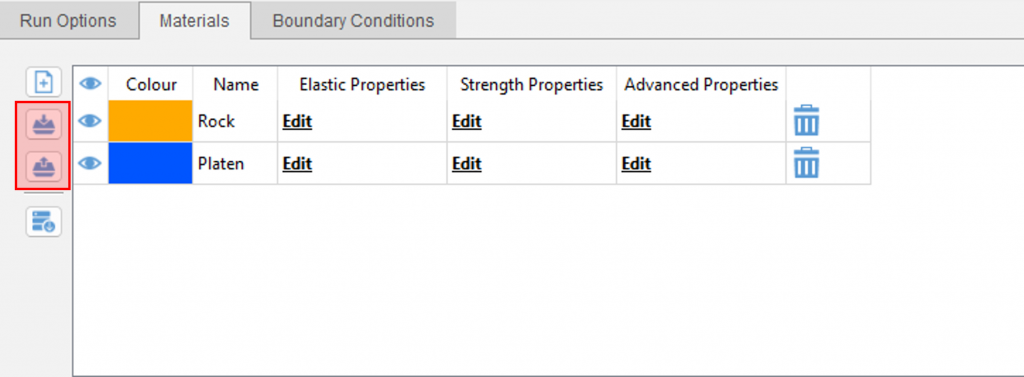
Location of import/export buttons under the materials/DFN tab. The user has the option to export the materials/DFN in JSON or CSV format and can import in JSON format.
Using the “Copy Into” function to duplicate material properties to another material set.
Check the imported CAD geometry
If importing CAD geometry, check for duplicate entities and ensure good mesh quality when embedding CAD geometry onto surfaces. Mesh quality can be improved by changing the meshing algorithm in Mesh > Mesh Options.
Using the appropriate contact options
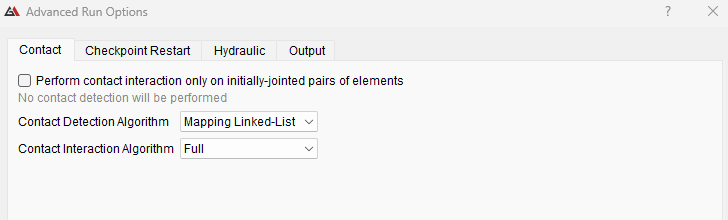
If utilized correctly, changes to contact settings under Model > Advanced Run Options > Contact can lead to significant savings in run time. Generally, the mapped linked-list Contact Detection Algorithm is faster for models with varying element sizes, while workdivision hash is faster for models with uniform element sizes. For models with very small expected strain and/or no material interfaces, only performing contact interaction at the beginning of the run will also lead to significant speed ups.
Restarting models from checkpoints
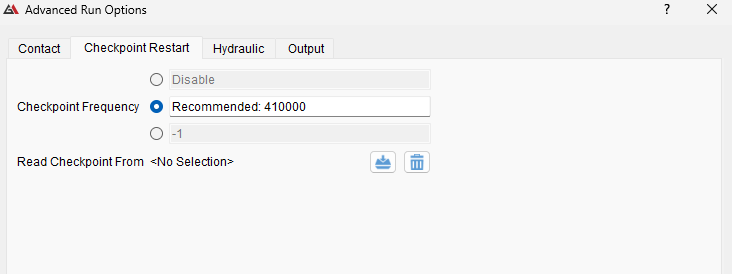
Unfortunately, computers and software sometimes unexpectedly crash and can result in abrupt termination of running models. Use the checkpoint restart feature in Model > Advanced Run Options > Checkpoint Restart to save complete model snapshots (checkpoints) and continue running the model from a saved checkpoint file.
Understanding Irazu file structure
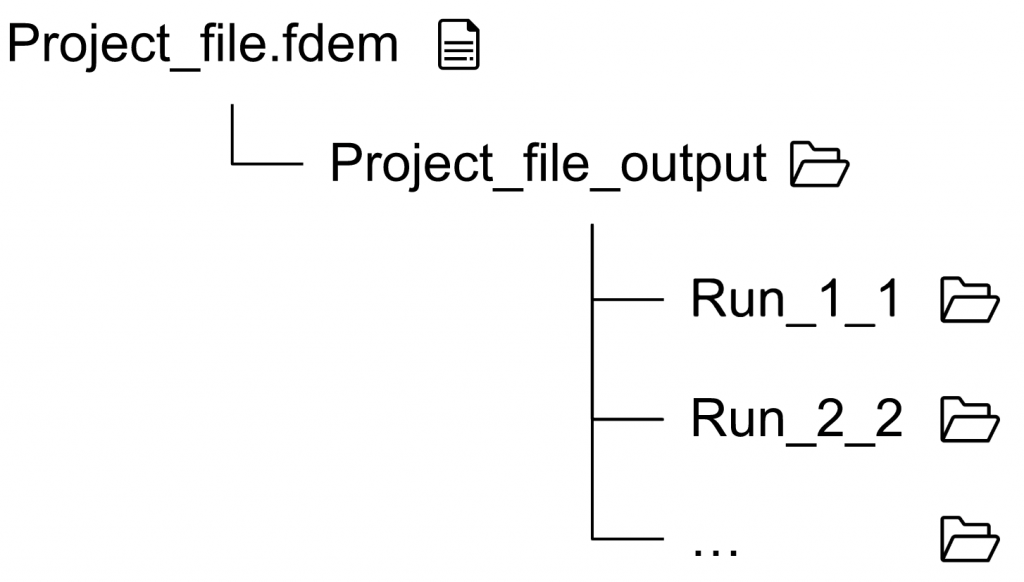
When you run a model in Irazu, an output folder is automatically created for that Run with the file structure shown to the right. Make sure to never remove, move, or rename the output folder(s) as this will break the link between the Runs in Irazu and the actual output files on the disk.